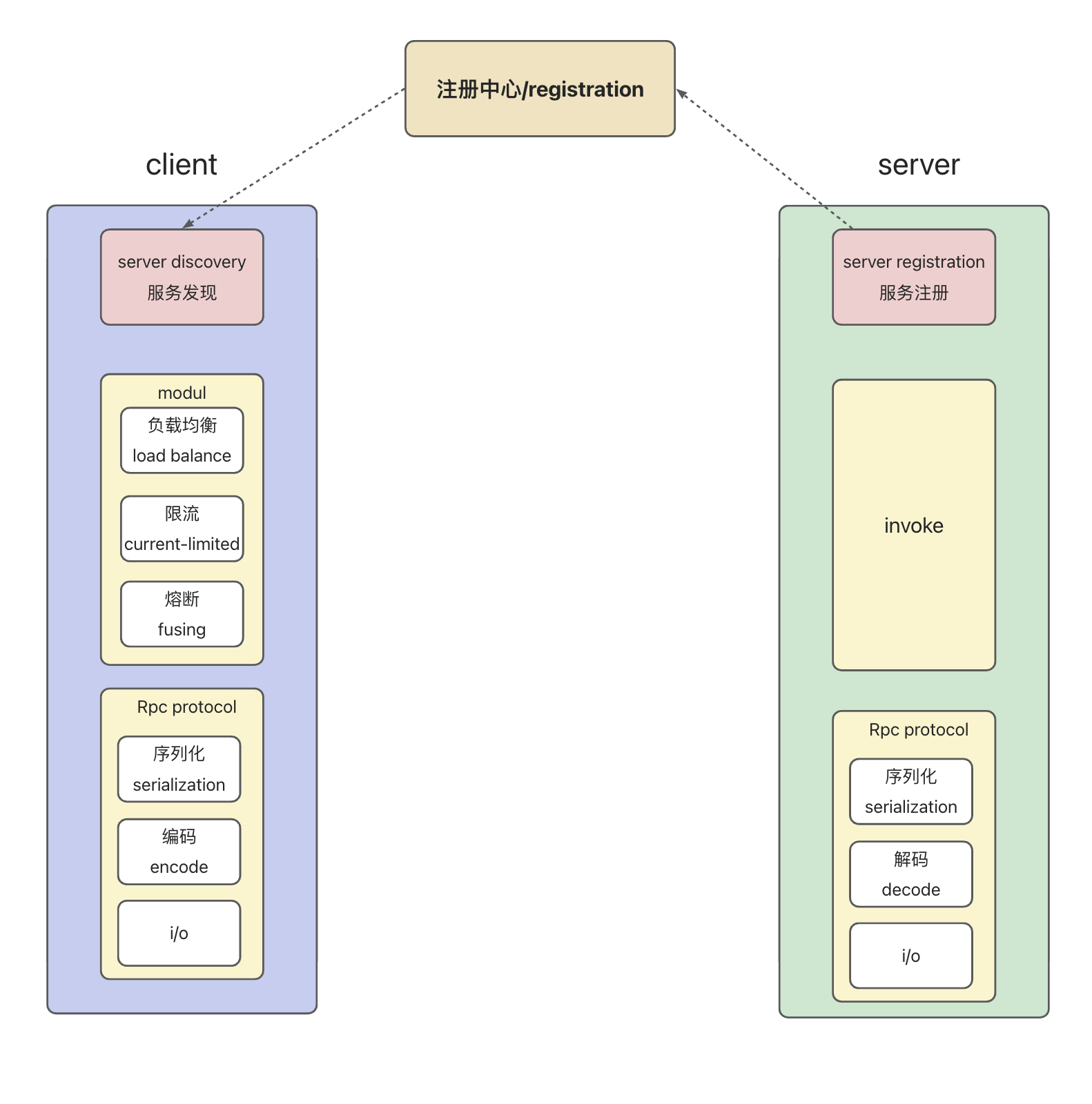
基于springBoot,手写一个简单的RPC框架(二)
继续上一章,实现了服务注册后需要实现服务调用。
服务执行 一个RPC的服务调用应该分为以下几步:
请求监听;
解码请求;
方法调用;
返回结果;
接下来将依次实现以上功能;
请求监听 需要定义一个RpcRequest请求类,由于后续处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor @Builder public class RpcRequest implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 8509587559718339795L ; private String traceId; private String serviceName; private String methodName; private Object[] parameters; private Class<?>[] paramTypes; private String version; private String project; private String group; public String fetchRpcServiceName () { return this .getProject() +"*" +this .getGroup()+"*" + this .getServiceName() +"*" + this .getVersion(); } }
监听请求需要启动一个netty server,用于监听请求service的服务。
启动时首先需要关闭之前注册的服务等资源。
随后对netty需要的资源进行依次初始化。
以下是一段netty的启动代码,其中需要加入编码和解码器用于协议解析,探活。
同时,需要加入限流和解码后的请求处理hanlder
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 @Component public class NettyServer { public NettyServer () { } public void start () { LogUtil.info("netty server init" ); ServerShutdownHook.getInstance().registerShutdownHook(); EventLoopGroup listenerGroup = initListenerGroup(); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = initWorkerGroup(); DefaultEventExecutorGroup businessGroup = initBusinessGroup(); LogUtil.info("netty server start" ); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = configureServerBootstrap(listenerGroup, workerGroup, businessGroup); bindAndListen(serverBootstrap); } catch (Exception e) { LogUtil.error("occur exception when start server:" , e); } finally { shutdown(listenerGroup, workerGroup, businessGroup); } } private EventLoopGroup initListenerGroup () { return new NioEventLoopGroup (1 ); } private EventLoopGroup initWorkerGroup () { return new NioEventLoopGroup (); } private DefaultEventExecutorGroup initBusinessGroup () { return new DefaultEventExecutorGroup ( Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2 , ThreadPoolFactoryUtil.createThreadFactory("netty-server-business-group" , false ) ); } private ServerBootstrap configureServerBootstrap (EventLoopGroup listenerGroup, EventLoopGroup workerGroup, DefaultEventExecutorGroup businessGroup) { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap (); serverBootstrap.group(listenerGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ) .childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true ) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .handler(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.INFO)) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler (30 , 0 , 0 , TimeUnit.SECONDS)); pipeline.addLast(new RpcMessageEncoder ()); pipeline.addLast(new RpcMessageDecoder ()); pipeline.addLast(new DefaultTrafficBlockHandler ()); pipeline.addLast(businessGroup, new NettyRpcServerHandler ()); } }); return serverBootstrap; } private void bindAndListen (ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap) throws UnknownHostException, InterruptedException { LogUtil.info("netty server bind port:{} " , PropertiesFileUtil.readPortFromProperties()); String host = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress(); ChannelFuture f = serverBootstrap.bind(host, PropertiesFileUtil.readPortFromProperties()).sync(); f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } private void shutdown (EventLoopGroup listenerGroup, EventLoopGroup workerGroup, DefaultEventExecutorGroup businessGroup) { listenerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); businessGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } @NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE) public class ServerShutdownHook { private static final ServerShutdownHook INSTANCE = new ServerShutdownHook (); public static ServerShutdownHook getInstance () { return INSTANCE; } public void registerShutdownHook () { Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread (() -> { clearAll(); })); } private void clearAll () { try { InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress (InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress(), PropertiesFileUtil.readPortFromProperties()); CuratorClient.clearRegistry(CuratorClient.getZkClient(), inetSocketAddress); } catch (Exception ignored) { } ThreadPoolFactoryUtil.shutDownAllThreadPool(); } }
结合ApplicationRunner,实现server的自动启动
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Component public class NettyServerRunner implements ApplicationRunner { @Autowired private NettyServer nettyServer; public NettyServerRunner () {} @Override public void run (ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { nettyServer.start(); } }
序列化 本项目默认只是实现了hessen的序列化和gzip加解压,这部分有许多的教程,所以在这里介绍。具体的代码可以在源码的org.example.ray.infrastructure.serialize包和org.example.ray.infrastructure.compress包中找到
编码与协议 实现了服务后,我们需要依次为他补充编码和处理类。
在实现编码的服务之前,首先应该确定底层的编码协议。
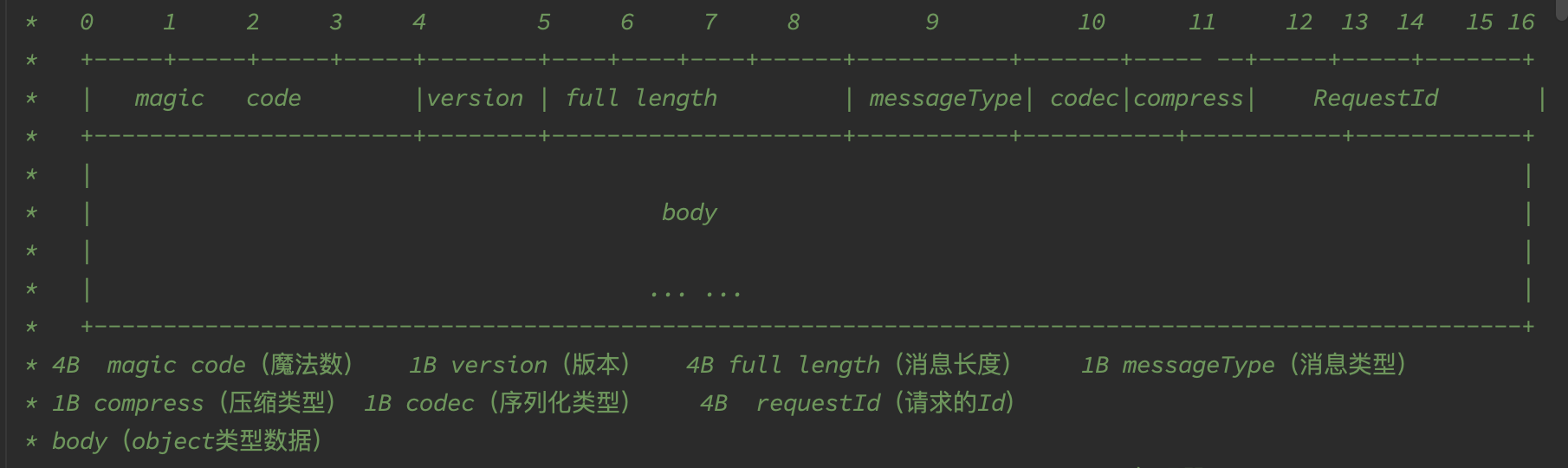
协议 本项目参考一些已有的协议设计,选择了一种比较简单的协议设计方式,如下图所示:
协议由一个16byte的header和body组成。
其中0-4是magic code,用于校验
4-5为自定义的协议版本
5-8是整个message的长度,用于解码
8-9定义了消息类型,包括请求,响应,心跳请求,心跳响应。
10为编码方式
11为压缩方式
12-16为一个整型,为请求的编号
Java pojo如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Builder public class RpcData { private byte messageType; private byte serializeMethodCodec; private byte compressType; private int requestId; private Object data; public boolean isHeatBeatRequest () { return messageType == RpcConstants.HEARTBEAT_REQUEST_TYPE; } public boolean canSendRequest () { return messageType != RpcConstants.HEARTBEAT_REQUEST_TYPE && messageType != RpcConstants.HEARTBEAT_RESPONSE_TYPE; } public boolean isHeartBeatResponse () { return messageType == RpcConstants.HEARTBEAT_RESPONSE_TYPE; } public boolean isResponse () { return messageType == RpcConstants.RESPONSE_TYPE; } }
在了解了协议之后,实现解码
解码 LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder解码器可以参考以下文章
1 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/95621344"
在了解LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder解码器的基础上,解码的过程其实并不复杂。主要是解码header,校验,和解码body3部分,具体实现可以参考代码和注释。
解码部分使用java spi,可以定制选择反序列化和解压方法,此部分可以参考github中的代码,或者可以只使用固定序列化和解压方法替代spi部分。
本项目默认只是实现了hessen的序列化和gzip加解压,这部分有许多的教程,所以在这里介绍。具体的代码可以在源码的org.example.ray.infrastructure.serialize包和org.example.ray.infrastructure.compress包中找到
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 public class RpcMessageDecoder extends LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder { public RpcMessageDecoder () { this (8 * 1024 * 1024 , 5 , 4 , -9 , 0 ); } public RpcMessageDecoder (int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength, int lengthAdjustment, int initialBytesToStrip) { super (maxFrameLength, lengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength, lengthAdjustment, initialBytesToStrip); } @Override protected Object decode (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception { Object decode = super .decode(ctx, in); if (decode instanceof ByteBuf) { ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf)decode; if (byteBuf.readableBytes() >= RpcConstants.HEAD_LENGTH) { try { return decode(byteBuf); } catch (Exception e) { LogUtil.error("Decode error:{} ,input:{}" , e, byteBuf); } finally { byteBuf.release(); } } } return decode; } private Object decode (ByteBuf byteBuf) { LogUtil.info("start decode" ); checkMagicCode(byteBuf); checkVersion(byteBuf); int fullLength = byteBuf.readInt(); RpcData rpcMessage = decodeRpcMessage(byteBuf); if (rpcMessage.isHeatBeatRequest()) { return handleHeatBeatRequest(rpcMessage); } if (rpcMessage.isHeartBeatResponse()) { return handleHeartBeatResponse(rpcMessage); } return handleNormalRequest(rpcMessage, byteBuf, fullLength); } private RpcData decodeRpcMessage (ByteBuf byteBuf) { LogUtil.info("start decode RpcMessage data" ); byte messageType = byteBuf.readByte(); byte codec = byteBuf.readByte(); byte compress = byteBuf.readByte(); int traceId = byteBuf.readInt(); return RpcData.builder() .serializeMethodCodec(codec) .traceId(traceId) .compressType(compress) .messageType(messageType) .build(); } private RpcData handleHeatBeatRequest (RpcData rpcMessage) { rpcMessage.setData(RpcConstants.PING); return rpcMessage; } private RpcData handleHeartBeatResponse (RpcData rpcMessage) { rpcMessage.setData(RpcConstants.PONG); return rpcMessage; } private Object handleNormalRequest (RpcData rpcMessage, ByteBuf byteBuf, int fullLength) { int bodyLength = fullLength - RpcConstants.HEAD_LENGTH; if (bodyLength <= 0 ) { return rpcMessage; } return decodeBody(rpcMessage, byteBuf, bodyLength); } private RpcData decodeBody (RpcData rpcMessage, ByteBuf byteBuf, Integer bodyLength) { LogUtil.info("start decode body" ); byte [] bodyBytes = new byte [bodyLength]; byteBuf.readBytes(bodyBytes); String compressName = CompressTypeEnum.getName(rpcMessage.getCompressType()); CompressService extension = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(CompressService.class).getExtension(compressName); bodyBytes = extension.decompress(bodyBytes); if (rpcMessage.getMessageType() == RpcConstants.REQUEST_TYPE) { RpcRequest rpcRequest = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(SerializationService.class) .getExtension(SerializationTypeEnum.getName(rpcMessage.getSerializeMethodCodec())) .deserialize(bodyBytes, RpcRequest.class); rpcMessage.setData(rpcRequest); } else { RpcResponse rpcResponse = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(SerializationService.class) .getExtension(SerializationTypeEnum.getName(rpcMessage.getSerializeMethodCodec())) .deserialize(bodyBytes, RpcResponse.class); rpcMessage.setData(rpcResponse); } return rpcMessage; } private void checkVersion (ByteBuf byteBuf) { byte version = byteBuf.readByte(); if (version != RpcConstants.VERSION) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("version is not compatible: " + version); } } private void checkMagicCode (ByteBuf byteBuf) { int length = RpcConstants.MAGIC_NUMBER.length; byte [] magicNumber = new byte [length]; byteBuf.readBytes(magicNumber); for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) { if (magicNumber[i] != RpcConstants.MAGIC_NUMBER[i]) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Unknown magic code: " + new String (magicNumber)); } } } }
编码 编码的过程相对简单,就是根据协议,依次将对应位的数据写入即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 public class RpcMessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder <RpcData> { private static final AtomicInteger ATOMIC_INTEGER = new AtomicInteger (0 ); @Override protected void encode (ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, RpcData rpcData, ByteBuf byteBuf) { try { int fullLengthIndex = encodeHead(rpcData,byteBuf); int fullLength = encodeBody(rpcData, byteBuf); encodeLength(fullLengthIndex,fullLength,byteBuf); } catch (Exception e) { LogUtil.error("Encode request error:{},data:{}" , e, rpcData); throw new RpcException (RpcErrorMessageEnum.REQUEST_ENCODE_FAIL.getCode(), RpcErrorMessageEnum.REQUEST_ENCODE_FAIL.getMessage()); } } private int encodeHead (RpcData rpcData,ByteBuf byteBuf) { byteBuf.writeBytes(RpcConstants.MAGIC_NUMBER); byteBuf.writeByte(RpcConstants.VERSION); int fullLengthIndex = byteBuf.writerIndex(); byteBuf.writerIndex(byteBuf.writerIndex() + 4 ); byteBuf.writeByte(rpcData.getMessageType()); byteBuf.writeByte(rpcData.getSerializeMethodCodec()); byteBuf.writeByte(rpcData.getCompressType()); byteBuf.writeInt(ATOMIC_INTEGER.getAndIncrement()); return fullLengthIndex; } private int encodeBody (RpcData rpcData,ByteBuf byteBuf) { byte [] bodyBytes = null ; int fullLength = RpcConstants.HEAD_LENGTH; if (rpcData.canSendRequest()) { LogUtil.info("serialize request start" ); bodyBytes = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(SerializationService.class) .getExtension(SerializationTypeEnum.getName(rpcData.getSerializeMethodCodec())) .serialize(rpcData.getData()); LogUtil.info("serialize request end" ); String compressName = CompressTypeEnum.getName(rpcData.getCompressType()); CompressService extension = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(CompressService.class).getExtension(compressName); bodyBytes = extension.compress(bodyBytes); fullLength += bodyBytes.length; } if (bodyBytes != null ) { byteBuf.writeBytes(bodyBytes); } return fullLength; } private void encodeLength (int fullLengthIndex,int fullLength,ByteBuf byteBuf) { int writeIndex = byteBuf.writerIndex(); byteBuf.writerIndex(fullLengthIndex); byteBuf.writeInt(fullLength); byteBuf.writerIndex(writeIndex); } }
请求处理和调用 这里实用netty的SimpleChannelInboundHandler,可以避免资源释放的问题
由于前面已经实现了解码,所以只需要针对不同的请求类型进行不同的处理即可。
如果是心跳请求,则返回心跳响应
如果是服务请求,则通过动态代理调用服务,并写入结果返回给消费者。
定义一个响应类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor @Data @Builder public class RpcResponse <T> implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 347966260947189201L ; private String requestId; private Integer code; private String message; private T data; public static <T> RpcResponse<T> success (T data, String requestId) { RpcResponse<T> response = new RpcResponse <>(); response.setCode(RpcResponseCodeEnum.SUCCESS.getCode()); response.setMessage(RpcResponseCodeEnum.SUCCESS.getMessage()); response.setRequestId(requestId); if (null != data) { response.setData(data); } return response; } public static <T> RpcResponse<T> fail () { RpcResponse<T> response = new RpcResponse <>(); response.setCode(RpcResponseCodeEnum.FAIL.getCode()); response.setMessage(RpcResponseCodeEnum.FAIL.getMessage()); return response; } }
serverhandler的核心方法为channelRead0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 public class NettyRpcServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler <RpcData> { private final RpcRequestHandler rpcRequestHandler; public NettyRpcServerHandler () { this .rpcRequestHandler = SingletonFactory.getInstance(RpcRequestHandler.class); } @Override public void userEventTriggered (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception { if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) { IdleState state = ((IdleStateEvent)evt).state(); if (state == IdleState.READER_IDLE) { LogUtil.info("idle check happen, so close the connection" ); ctx.close(); } } else { super .userEventTriggered(ctx, evt); } } @Override public void exceptionCaught (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) { LogUtil.error("server exceptionCaught" ); cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcData rpcData) throws Exception { LogUtil.info("Server receive message: [{}]" , rpcData); RpcData rpcMessage = new RpcData (); setupRpcMessage(rpcMessage); if (rpcData.isHeatBeatRequest()) { handleHeartbeat(rpcMessage); } else { handleRpcRequest(ctx, rpcData, rpcMessage); } ctx.writeAndFlush(rpcMessage).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE); } private void setupRpcMessage (RpcData rpcMessage) { rpcMessage.setSerializeMethodCodec(SerializationTypeEnum.HESSIAN.getCode()); rpcMessage.setCompressType(CompressTypeEnum.GZIP.getCode()); } private void handleHeartbeat (RpcData rpcMessage) { rpcMessage.setMessageType(RpcConstants.HEARTBEAT_RESPONSE_TYPE); rpcMessage.setData(RpcConstants.PONG); } private void handleRpcRequest (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcData rpcData, RpcData rpcMessage) throws Exception { RpcRequest rpcRequest = (RpcRequest)rpcData.getData(); Object result = rpcRequestHandler.handle(rpcRequest); LogUtil.info("Server get result: {}" , result); rpcMessage.setMessageType(RpcConstants.RESPONSE_TYPE); buildAndSetRpcResponse(ctx, rpcRequest, rpcMessage, result); } private void buildAndSetRpcResponse (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcRequest rpcRequest, RpcData rpcMessage, Object result) { if (canBuildResponse(ctx)) { RpcResponse<Object> rpcResponse = RpcResponse.success(result, rpcRequest.getTraceId()); rpcMessage.setData(rpcResponse); } else { RpcResponse<Object> rpcResponse = RpcResponse.fail(); rpcMessage.setData(rpcResponse); LogUtil.error("Not writable now, message dropped,message:{}" , rpcRequest); } } private boolean canBuildResponse (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { return ctx.channel().isActive() && ctx.channel().isWritable(); } }
tipp: 注册到zk后缓存的服务,可以直接基于动态代理进行调用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public class RpcRequestHandler { private final RpcServiceRegistryAdapter adapter; public RpcRequestHandler () { this .adapter = SingletonFactory.getInstance(RpcServiceRegistryAdapterImpl.class); } public Object handle (RpcRequest request) { Object service = adapter.getService(request.fetchRpcServiceName()); return invoke(request, service); } private Object invoke (RpcRequest rpcRequest, Object service) { Object result; try { Method method = service.getClass().getMethod(rpcRequest.getMethodName(), rpcRequest.getParamTypes()); result = method.invoke(service, rpcRequest.getParameters()); LogUtil.info("service:[{}] successful invoke method:[{}]" , rpcRequest.getServiceName(), rpcRequest.getMethodName()); } catch (NoSuchMethodException | IllegalArgumentException | InvocationTargetException | IllegalAccessException e) { LogUtil.error("occur exception when invoke target method,error:{},RpcRequest:{}" , e, rpcRequest); throw new RpcException (RpcErrorMessageEnum.SERVICE_INVOCATION_FAILURE.getCode(), RpcErrorMessageEnum.SERVICE_INVOCATION_FAILURE.getMessage()); } return result; } }
至此,一个服务端的代码就完成了