树状数组与力扣中的应用
为什么会需要树状数组
QA:
假设存在一个整数序列input,例如
intput = [1,2,7,4,3],要求前K个数的和。Sulotion:
一般我们会求一个前缀和数组
preSumArray,其中preSumArray[i]代表前i个数的和,这样我们求前N个数的和只需要返回preSumArray[N], 时间复杂度为O(1),如果需要查询K次,则复杂度为O(K).QA:
假设存在一个整数序列input,例如
intput = [1,2,7,4,3],现在在我们获取前N个数的和时,可能会先将i位置的数增加/减少value。Sulotion:
一般我们会求一个前缀和数组
preSumArray,其中preSumArray[i]代表前i个数的和,如上一个问题所示,我们依旧可以在O(1)的时间得到前缀和。但是如果我们需要在第i位置插入一个数x,在进行更新时需要更新i之后的所有preSumArray,此时单次的更新时间为O(N),K次查询的复杂度为O(KN)。如果我们不使用preSumArray,那么更新复杂度为O(1),查询复杂度会变为O(N)。这时树桩数组可以帮助我们快速解决这个问题
二进制有很多有趣的应用,可能后续可以进行一些总结,但是这里介绍一个用法
lowbit(x) = x&(-x)这个式子的目的是可以求出能够整除X的最大的2次幂,也就是X最右边的1,这个目的很重要。
举个例子:
5&-5 = 1;10&-10 = 2;12&-12 = 4原理:
一般整数在计算机中使用补码存储,负数相当于每一位取反,然后低位+1。
如
10 = 1010,-10 = 0110,因此lowbit(10) = 2数状数组(Binary Indexed Tree,BIT)
本质上它仍是一个数组,并且与
preSumArray相似,存的依旧是和数组,但是他存放的是 i位之前(包括i),lowbit(i)个整数的和。可以用下图以及公式表示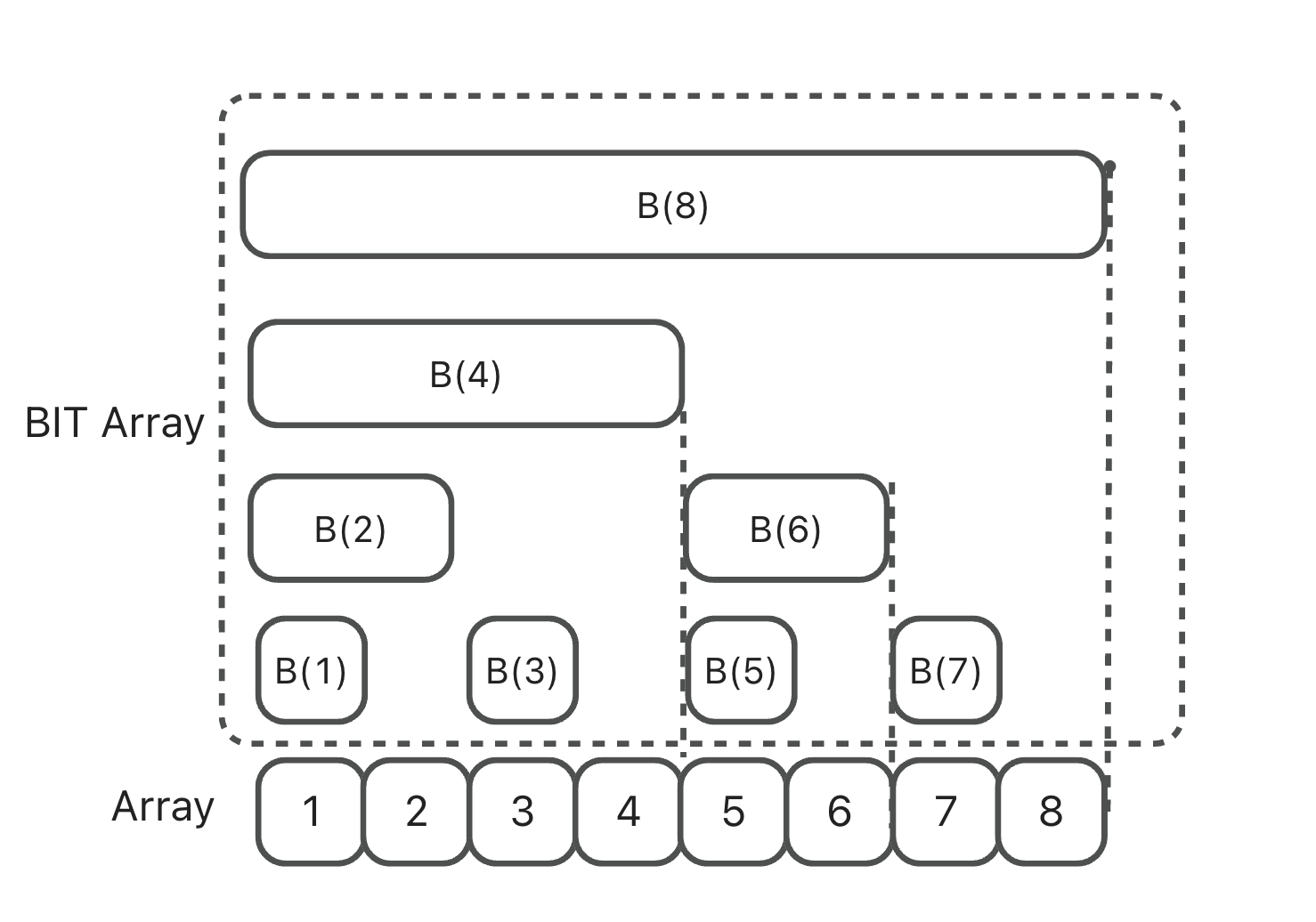
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9B(1) = A(1);
B(2) = A(1)+A(2);
B(3) = A(3);
B(4) = A(1)+A(2)+A(3)+A(4);
B(5) = A(5);
B(6) = A(5)+A(6);
B(7) = A(7);
B(8) = A(1)+A(2)+A(3)+A(4)+A(5)+A(6)+A(7)+A(8);tip:树状数组的下标必须从1开始
使用
现在基于树状数组,我们需要解决之前的2个问题——求和与更新。
求和
假设我们有一个函数getSum(i),可以求1-i的所有数的和。接下来就是如何去实现它。
举个例子:
getSum(7) = A(1)+...+A(7) = B(4)+B(6)+B(7)getSum(6) = B(4)+B(6)现在的问题就是,如何将
A(1)+....+A(i)映射到树桩数组对应那些项:
首先: B(i)的定义为从A(i)开始,前lowbit(i)的和,所以我们可以得到
$B(i) = A(i-lowbit(i)+1)+…+A(i)$
因此,我们可以得到:$$getSum(i) = A(1)+…+A(i)\
=A(1)+…+A(i-lowbit(i))+A(i-lowbit(i)+1)+…+A(i)\
=getSum(i-lowbit(i))+B(i)$$这样我们可以很容易的写出getSum函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public int getSum(int x){
int res = 0;
for(int i = x; i > 0; i -= lowbit(i)) {
res += bit[i];
}
return res;
}使用递归的形式:
1
2
3
4
5
6public int getSum(int x){
if(x<=0){
return 0;
}
return bit[x]+(long)getSum(x-lowbit(x));
}该过程的复杂度为O(LogN)(省略过程)
更进一步,如果我们要求
sum(i,j),那么我们只需要getSum(j)-getSum(i-1)即可。更新
假设我们有一个函数
update(i,value),实现在i位置的数加上value。现在思考如何实现:还是举个例子:
如果我们要
update(6,7),也就是在6的位置+7,那我们根据上面的图,我们需要更新B(6)和B(8),因为B(6)和B(8)的求和项均包含了A(6)。B(6) = A(5)+A(6);B(8) = A(1)+A(2)+A(3)+A(4)+A(5)+A(6)+A(7)+A(8);所以现在的问题转换为如何知道BIT中所有包含A(i)的项。

比如我们我们要找到所有覆盖A(5)的BIT。
首先:B(5)一定覆盖了。
其次,我们需要找到距离B(5)最近覆盖它的BIT,即B(6)
接下来只需要找到覆盖了B(6)距离他最近的BIT,即B(8)
以此类推。
也就是说,我们只需要找到对于当前BIT(i),能覆盖它的最近的BIT(j),并更新他的值。
我们可以发现:
如果需要BIT(j)覆盖BIT(i),那么
lowbit(j)>lowbit(i),否则肯定无法覆盖,那么可以转换为lowbit(i+a)>lowbit(i),求最小的a。因为lowbit(i)是整除i的最大的2次幂,也就是i最右边的1。
所以如果
lowbit(a)<lowbit(i),那么lowbit(i+a)<lowbit(i)。举个例子,如果
lowbit(j)是0100,lowbit(i)是0010,如果lowbit(a+i)一定小于lowbit(i)(因为最右边的1一定会被保留所以a+i只会取a和i中右1更小的那个)。当
lowbit(a)=lowbit(i),此时会最右边的1会产生进位,那么最右边的1一定会向右移,所以lowbit(a+i)>lowbit(i),一定成立,因此我们可以得到lowbit(a)=lowbit(i)这样我们可以开始写update函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6public void updata(int x,int value){
for(int i = x; i < bit.length; i += lowbit(i)){
//update
bit[i] += value;
}
}
力扣中的应用
LeetCode-493
Qa:
给定一个数组
nums,如果i < j且nums[i] > 2*nums[j]我们就将(i, j)称作一个重要翻转对\。你需要返回给定数组中的重要翻转对的数量。
Input:
1
2输入: [1,3,2,3,1]
输出: 2Solution
题干的问题可以转换为求 在j元素左边比他2倍大的元素有几个,并求和。
- 将数组进行排序,并且离散化映射为1-n的有序序列(多数题都需要这一步,因为树状数组的索引必须从1开始,所以需要对入参进行映射)。
- 统计每个数的出现次数。
- 求映射元素次数的前缀和, 得到映射后的元素的个数, 也就得到了之前元素的个数
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61class Solution {
class TrieArr{
long [] arr;
public TrieArr(int n){
arr = new long [n];
}
public int lowbit(int x){
return x&(-x);
}
public int getSum(int x){
if(x<=0){
return 0;
}
return arr[x]+()getSum(x-lowbit(x));
}
public void updata(int x,int c){
for(int i = x; i < arr.length; i += lowbit(i)) arr[i] += c;
}
}
public int reversePairs(int[] nums) {
//nums[i] 和树桩数组的index映射map
//nums[i] and BIT's index mapping map
Map<Long,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
//对nums元素排序存储,因为要求的是大2倍的数,所以需要把nums[i]*2也加入计算
//Sort and store the elements of nums, because the number required is 2 times larger, so you need to add nums[i]*2 to the calculation as well
TreeSet<Long> set = new TreeSet<>();
for(int i:nums){
set.add((long)i);
set.add((long)i*2);
}
//离散化,并映射
//Discretization, and mapping
int index = 1;
while(!set.isEmpty()){
map.put(set.pollFirst(),index++);
}
//init bit tree
TrieArr bit = new TrieArr(map.size()+1);
//result
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
//因为是求大于nums[i]*2的出现总次数,那么将所有数字的出现次数-小于等于nums[i]*2出现的次数即可。
//Since we are looking for the total number of occurrences greater than nums[i]*2, it is sufficient to take the number of occurrences of all numbers - the number of occurrences less than or equal to nums[i]*2.
//get the nums[i]*2
long target = (long)nums[i] * 2;
//get bit index
int l = map.get(target);
//total sum - getsum(target)
ans += bit.getSum(map.size()) - bit.getSum(l);
//get nums[i]’s index and update nums[i] occurrences
bit.updata(map.get((long)nums[i]), 1);
}
return ans;
}
}
- #### 类似的问题还有LeetCode-307 .etc