KMP算法:
KMP (Knuth-Morris-Pratt) 算法是一种用于字符串搜索的算法,可以在一个文本串S内查找一个词W的出现位置。
基本思想是,当子串与目标字符串不匹配时,其已知足够的信息能确定下一步的搜索不会导致目标字符串的漏检。这样,算法就不会进行无效的检查。
下面是KMP算法的步骤:
- 构造一个”部分匹配表”(也称为 “失败函数”)。这是一个数组,对于给定的查找词,表中的每个元素都包含了当匹配失败时查找词应该跳转的位置。
- 使用这个表来进行字符串搜索。当在文本串中发生匹配失败时,可以直接跳过前面已知不会匹配的部分。
Why KMP
传统的字符串匹配,如果从String[i]的比较失败,算法直接开始尝试从S[i+1]进行比较。这种行为是典型的 “不从以前的错误中学习”。我们应该注意到,一个失败的匹配将为我们提供有价值的信息–如果String[i : i+len(P)]和P之间的匹配在第r个位置失败,那么从S[i]:第一个(r-1)连续字符必须与P的第一个(r-1)字符完全相同。
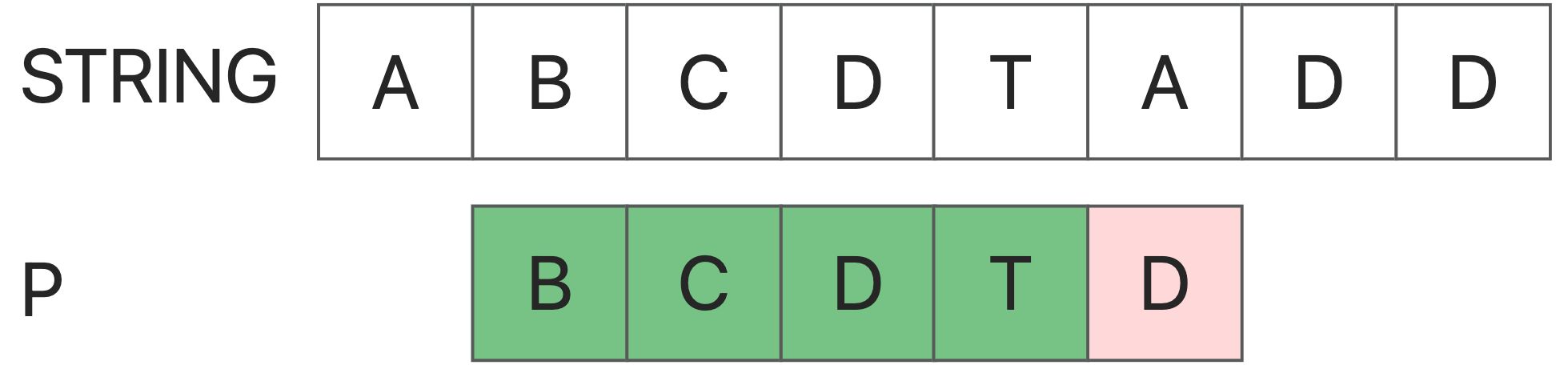
因此,我们可以尽可能地跳过这些不可能的字符串来优化我们的方法。
举个例子:
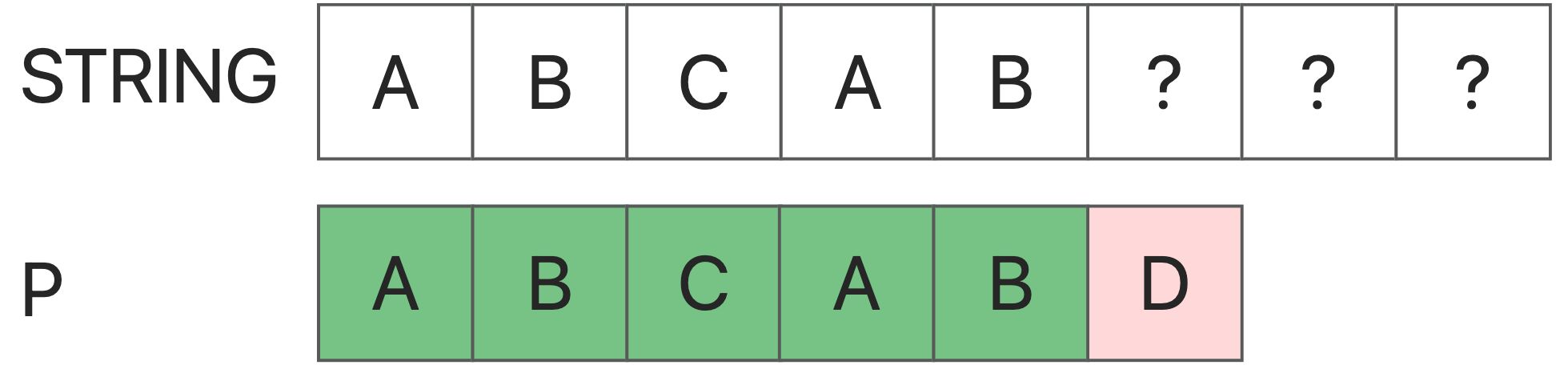
首先,P[5]未能匹配,那么这意味着S[0:5]等于P[0:5],也就是 “abcab”。
现在我们考虑:从S[1],S[2],S[3]最初的匹配尝试是否有机会成功?
当我们从S[1]开始时,它不会成功。因为我们可以看到:P[1]!=P[0],但P[1]=S[1],所以P[0]!=S[1]。
在S[2]中也是如此。
但是当我们从S[3]开始时(这很重要): P[0] = P[3], S[3] = P[3], 所以P[0] = S[3].
我们可以发现,在S[3]中,有可能匹配成功。而且我们会发现,如果知道S和P在长度L内是相同的,那么任何一个i是否可以作为匹配的起点,只取决于P[0]=P[i]是否相等。这里我们可以得到KMP算法的核心下一个数组
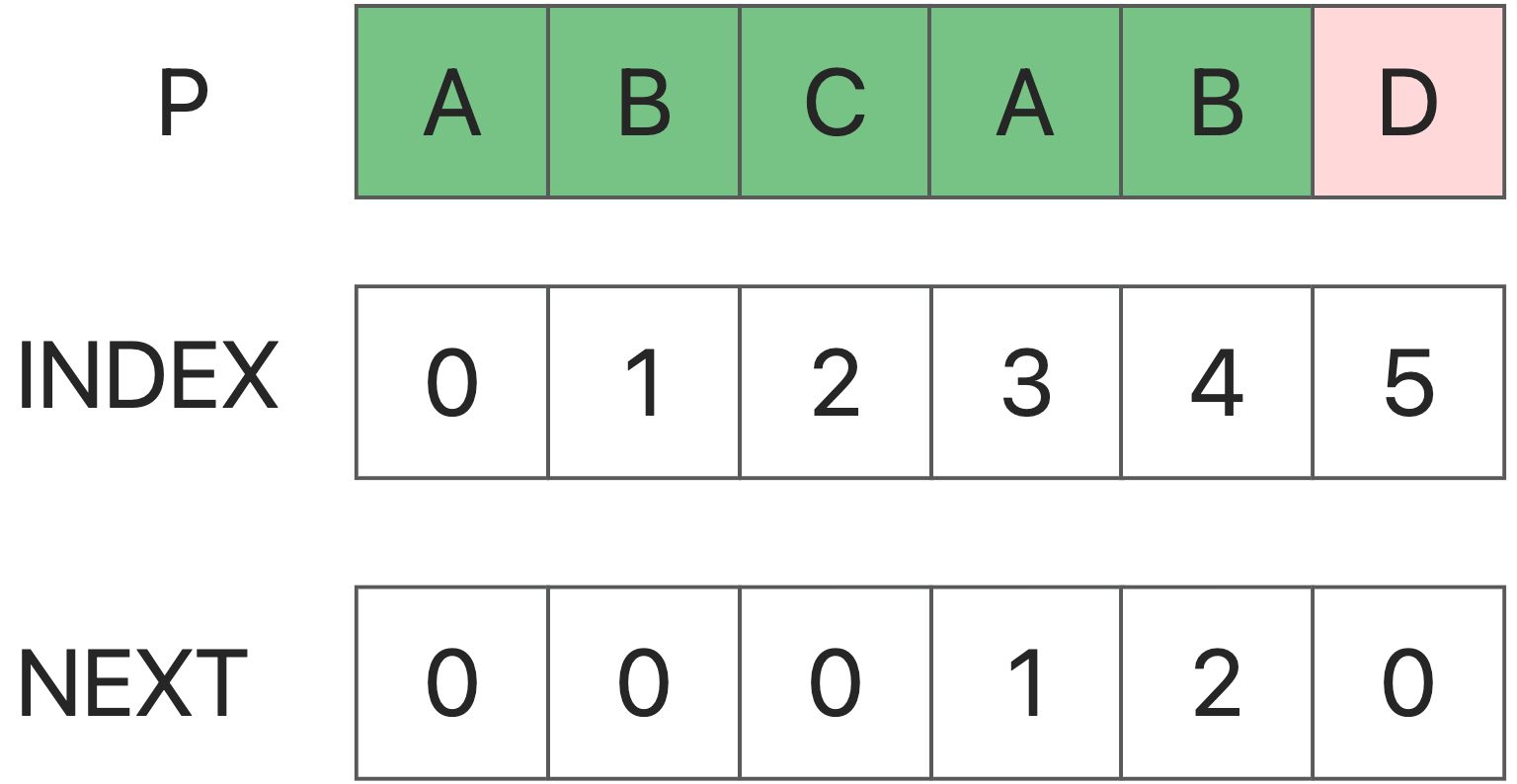
NextArray
下一个数组是用于模式字符串。P的下一个数组定义为:: next[i]代表P[0]~P[i]的一个子串,因此前k个字符正好等于后k个字符的最大k。特别是,k不能是i+1 (因为这个子串总共只有i+1个字符,它必须等于它自己,所以它没有意义)。 事实上,它是为了得到不同起点i时P串中最长的相同前缀和后缀的最大长度。
匹配
1 | int i=0; |
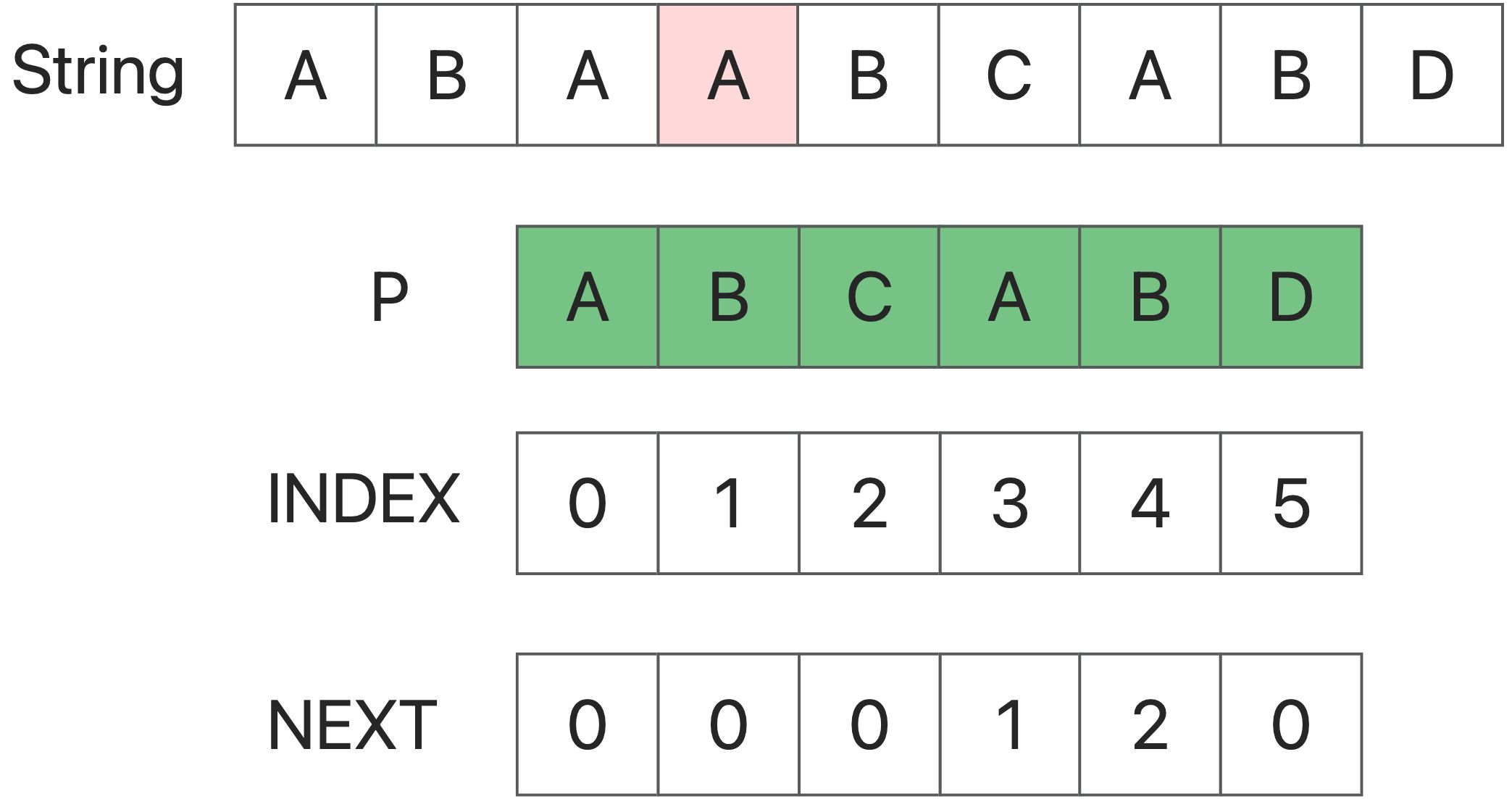
首先:我们使用两个点来捕捉字符串。问题是如何改变这个点?
第二:
String[i] != P [j] ,现在我们需要改变j来找到一个新的开始,即String的前缀等同于P。所以,下一个数组是有用的:` j = next[j]`。
如何获得下一个数组
1 | void getNext(String p, int [] next) |
这段代码使用了一个小技巧:使next[0]=-1.你可以记住它,这将使代码更加容易;
动态规划:
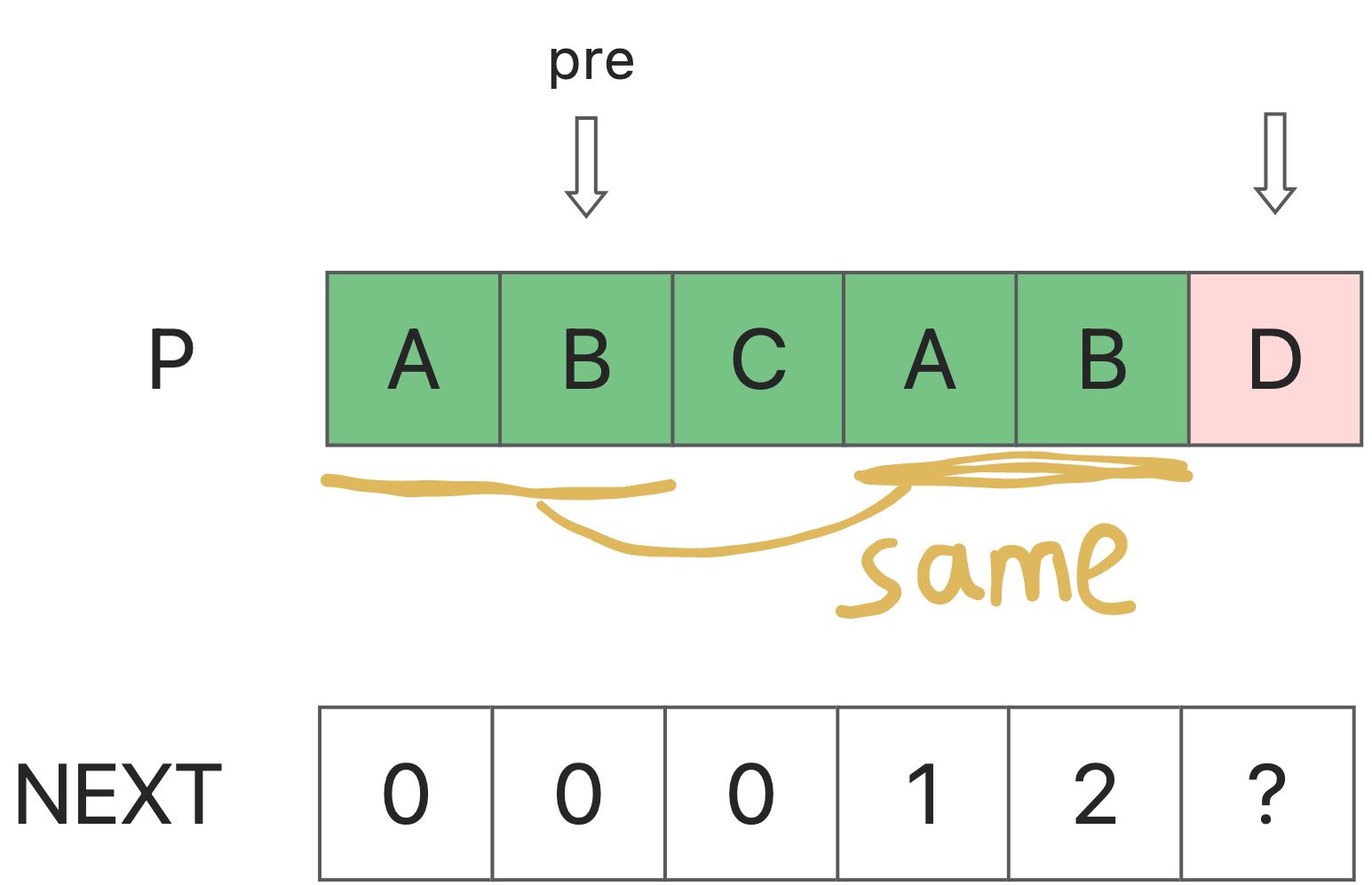
next[i]是指p[0,next[i]]=p[i-next[i],i]的最大值(i)
那么,如果我们知道next[0],next[1],…next[i-1],如何知道next[i]?
设置next[i-1] = pre。
如果p[i]=p[pre+1],这意味着下一个[i]=pre+1。
否则如果p[i] != p[pre+1],就意味着p[i-pre-1,i-1] = p[pre-1]。
我们应该减少pre:pre = next[pre]。
Code:
1 | /** |