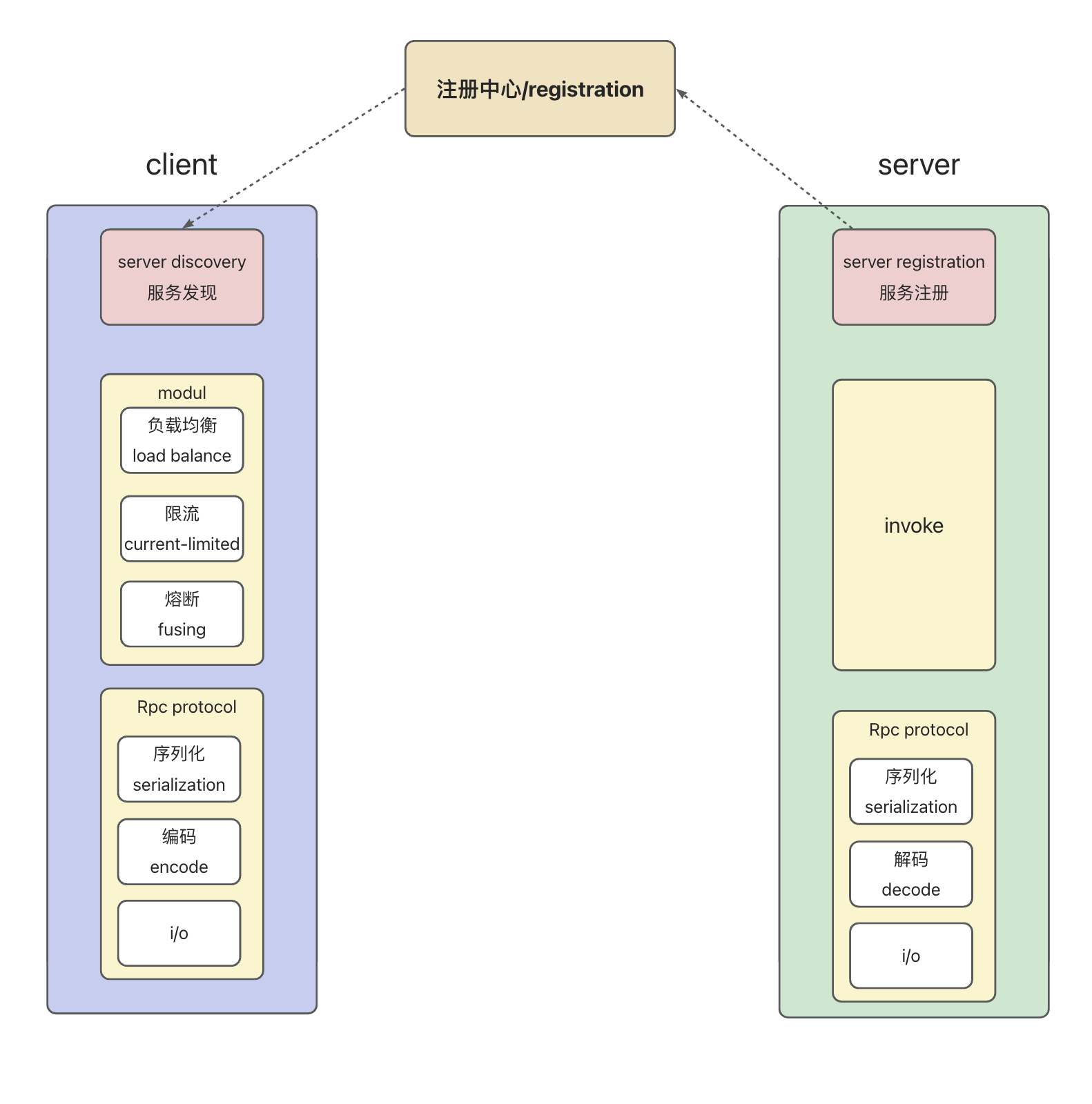
based on springBoot, hand-written a simple RPC framework(2)
Continuing from the previous chapter, after implementing the service registration you need to implement the service invocation.
Service execution An RPC service call should be divided into the following steps:
Request listening;
Decoding the request;
Method invocation;
Return of results;
The above functions will be implemented in turn;
Request Listening An RpcRequest request class needs to be defined, due to the subsequent processing of
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor @Builder public class RpcRequest implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 8509587559718339795L ; private String traceId; private String serviceName; private String methodName; private Object[] parameters; private Class<?>[] paramTypes; private String version; private String project; private String group; public String fetchRpcServiceName () { return this .getProject() +"*" +this .getGroup()+"*" + this .getServiceName() +"*" + this .getVersion(); } }
Listening for requests requires starting a netty server, which is used to listen for requests for service.
The start-up first requires the closure of previously registered resources such as services.
The resources required by netty are then initialised in turn.
The following is a snippet of netty startup code, which requires the addition of encoders and decoders for protocol parsing and probing.
At the same time, the request processing hanlder needs to be added for stream limiting and decoding.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 @Component public class NettyServer { public NettyServer () { } public void start () { LogUtil.info("netty server init" ); ServerShutdownHook.getInstance().registerShutdownHook(); EventLoopGroup listenerGroup = initListenerGroup(); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = initWorkerGroup(); DefaultEventExecutorGroup businessGroup = initBusinessGroup(); LogUtil.info("netty server start" ); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = configureServerBootstrap(listenerGroup, workerGroup, businessGroup); bindAndListen(serverBootstrap); } catch (Exception e) { LogUtil.error("occur exception when start server:" , e); } finally { shutdown(listenerGroup, workerGroup, businessGroup); } } private EventLoopGroup initListenerGroup () { return new NioEventLoopGroup (1 ); } private EventLoopGroup initWorkerGroup () { return new NioEventLoopGroup (); } private DefaultEventExecutorGroup initBusinessGroup () { return new DefaultEventExecutorGroup ( Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2 , ThreadPoolFactoryUtil.createThreadFactory("netty-server-business-group" , false ) ); } private ServerBootstrap configureServerBootstrap (EventLoopGroup listenerGroup, EventLoopGroup workerGroup, DefaultEventExecutorGroup businessGroup) { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap (); serverBootstrap.group(listenerGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ) .childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true ) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .handler(new LoggingHandler (LogLevel.INFO)) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler (30 , 0 , 0 , TimeUnit.SECONDS)); pipeline.addLast(new RpcMessageEncoder ()); pipeline.addLast(new RpcMessageDecoder ()); pipeline.addLast(new DefaultTrafficBlockHandler ()); pipeline.addLast(businessGroup, new NettyRpcServerHandler ()); } }); return serverBootstrap; } private void bindAndListen (ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap) throws UnknownHostException, InterruptedException { LogUtil.info("netty server bind port:{} " , PropertiesFileUtil.readPortFromProperties()); String host = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress(); ChannelFuture f = serverBootstrap.bind(host, PropertiesFileUtil.readPortFromProperties()).sync(); f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } private void shutdown (EventLoopGroup listenerGroup, EventLoopGroup workerGroup, DefaultEventExecutorGroup businessGroup) { listenerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); businessGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } @NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE) public class ServerShutdownHook { private static final ServerShutdownHook INSTANCE = new ServerShutdownHook (); public static ServerShutdownHook getInstance () { return INSTANCE; } public void registerShutdownHook () { Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread (() -> { clearAll(); })); } private void clearAll () { try { InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress (InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress(), PropertiesFileUtil.readPortFromProperties()); CuratorClient.clearRegistry(CuratorClient.getZkClient(), inetSocketAddress); } catch (Exception ignored) { } ThreadPoolFactoryUtil.shutDownAllThreadPool(); } }
Automatic start of the server in combination with ApplicationRunner
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Component public class NettyServerRunner implements ApplicationRunner { @Autowired private NettyServer nettyServer; public NettyServerRunner () {} @Override public void run (ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { nettyServer.start(); } }
serialization This project only implements hessen serialization and gzip plus decompression by default, there are many tutorials for this part, so it is presented here. The specific code can be found in the org.example.ray.infrastructure.serialize package and the org.example.ray.infrastructure.compress package in the source code
Coding and protocols Once the service has been implemented, we need to supplement him with encoding and processing classes in turn.
Before implementing the encoded service, the underlying encoding protocol should first be determined.
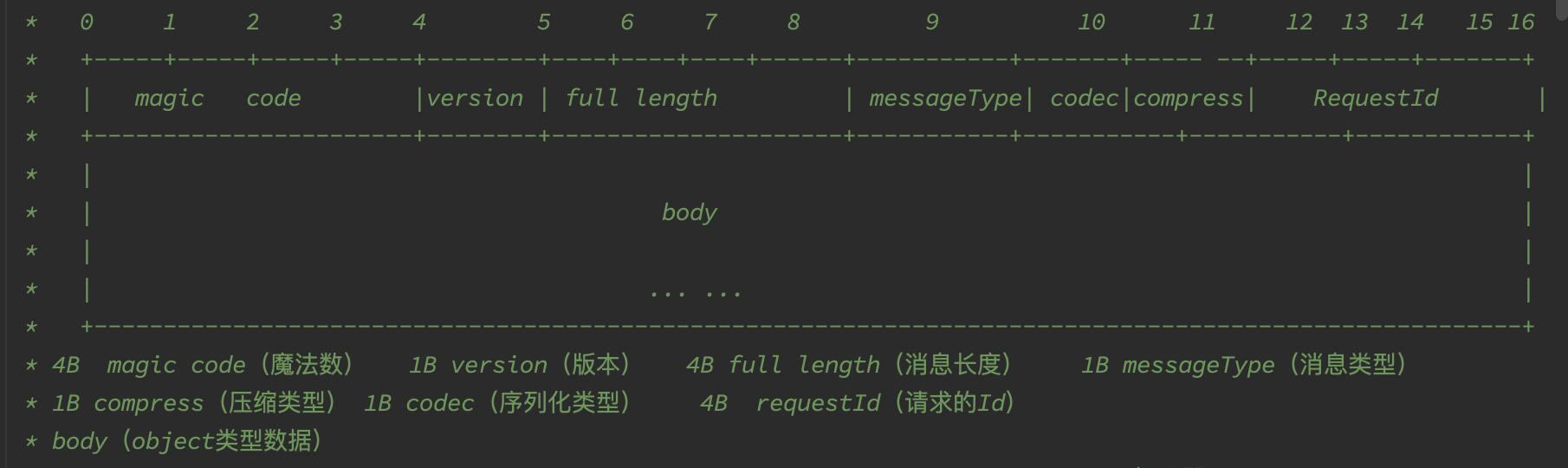
protocols For this project, we have chosen a relatively simple protocol design by referring to some existing protocol designs, as shown in the following diagram.
The protocol consists of a 16byte header and body.
Where 0-4 is the magic code, used for checksum
4-5 are custom versions of the protocol
5-8 is the length of the entire message, used for decoding
8-9 defines the message type, including request, response, heartbeat request, heartbeat response.
10 is the encoding method
11 is the compression method
12-16 is an integer for the number of the request
The Java pojo is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Builder public class RpcData { private byte messageType; private byte serializeMethodCodec; private byte compressType; private int requestId; private Object data; public boolean isHeatBeatRequest () { return messageType == RpcConstants.HEARTBEAT_REQUEST_TYPE; } public boolean canSendRequest () { return messageType != RpcConstants.HEARTBEAT_REQUEST_TYPE && messageType != RpcConstants.HEARTBEAT_RESPONSE_TYPE; } public boolean isHeartBeatResponse () { return messageType == RpcConstants.HEARTBEAT_RESPONSE_TYPE; } public boolean isResponse () { return messageType == RpcConstants.RESPONSE_TYPE; } }
After understanding the protocol, implement the decoding
decoding The LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder decoder can be found in the following article
1 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/95621344"
On the basis of understanding the LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder decoder, the decoding process is actually not complicated. It is mainly decoding header, checksum, and decoding body 3 parts, the specific implementation can refer to the code and comments.
The decoding part uses java spi, and can be customized to choose deserialization and decompression methods, this part can refer to the code in github, or can only use fixed serialization and decompression methods instead of spi part.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 public class RpcMessageDecoder extends LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder { public RpcMessageDecoder () { this (8 * 1024 * 1024 , 5 , 4 , -9 , 0 ); } public RpcMessageDecoder (int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength, int lengthAdjustment, int initialBytesToStrip) { super (maxFrameLength, lengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength, lengthAdjustment, initialBytesToStrip); } @Override protected Object decode (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception { Object decode = super .decode(ctx, in); if (decode instanceof ByteBuf) { ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf)decode; if (byteBuf.readableBytes() >= RpcConstants.HEAD_LENGTH) { try { return decode(byteBuf); } catch (Exception e) { LogUtil.error("Decode error:{} ,input:{}" , e, byteBuf); } finally { byteBuf.release(); } } } return decode; } private Object decode (ByteBuf byteBuf) { LogUtil.info("start decode" ); checkMagicCode(byteBuf); checkVersion(byteBuf); int fullLength = byteBuf.readInt(); RpcData rpcMessage = decodeRpcMessage(byteBuf); if (rpcMessage.isHeatBeatRequest()) { return handleHeatBeatRequest(rpcMessage); } if (rpcMessage.isHeartBeatResponse()) { return handleHeartBeatResponse(rpcMessage); } return handleNormalRequest(rpcMessage, byteBuf, fullLength); } private RpcData decodeRpcMessage (ByteBuf byteBuf) { LogUtil.info("start decode RpcMessage data" ); byte messageType = byteBuf.readByte(); byte codec = byteBuf.readByte(); byte compress = byteBuf.readByte(); int traceId = byteBuf.readInt(); return RpcData.builder() .serializeMethodCodec(codec) .traceId(traceId) .compressType(compress) .messageType(messageType) .build(); } private RpcData handleHeatBeatRequest (RpcData rpcMessage) { rpcMessage.setData(RpcConstants.PING); return rpcMessage; } private RpcData handleHeartBeatResponse (RpcData rpcMessage) { rpcMessage.setData(RpcConstants.PONG); return rpcMessage; } private Object handleNormalRequest (RpcData rpcMessage, ByteBuf byteBuf, int fullLength) { int bodyLength = fullLength - RpcConstants.HEAD_LENGTH; if (bodyLength <= 0 ) { return rpcMessage; } return decodeBody(rpcMessage, byteBuf, bodyLength); } private RpcData decodeBody (RpcData rpcMessage, ByteBuf byteBuf, Integer bodyLength) { LogUtil.info("start decode body" ); byte [] bodyBytes = new byte [bodyLength]; byteBuf.readBytes(bodyBytes); String compressName = CompressTypeEnum.getName(rpcMessage.getCompressType()); CompressService extension = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(CompressService.class).getExtension(compressName); bodyBytes = extension.decompress(bodyBytes); if (rpcMessage.getMessageType() == RpcConstants.REQUEST_TYPE) { RpcRequest rpcRequest = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(SerializationService.class) .getExtension(SerializationTypeEnum.getName(rpcMessage.getSerializeMethodCodec())) .deserialize(bodyBytes, RpcRequest.class); rpcMessage.setData(rpcRequest); } else { RpcResponse rpcResponse = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(SerializationService.class) .getExtension(SerializationTypeEnum.getName(rpcMessage.getSerializeMethodCodec())) .deserialize(bodyBytes, RpcResponse.class); rpcMessage.setData(rpcResponse); } return rpcMessage; } private void checkVersion (ByteBuf byteBuf) { byte version = byteBuf.readByte(); if (version != RpcConstants.VERSION) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("version is not compatible: " + version); } } private void checkMagicCode (ByteBuf byteBuf) { int length = RpcConstants.MAGIC_NUMBER.length; byte [] magicNumber = new byte [length]; byteBuf.readBytes(magicNumber); for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) { if (magicNumber[i] != RpcConstants.MAGIC_NUMBER[i]) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Unknown magic code: " + new String (magicNumber)); } } } }
Encoding The encoding process is relatively simple, it is just a matter of writing the corresponding bits of data in sequence according to the protocol
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 public class RpcMessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder <RpcData> { private static final AtomicInteger ATOMIC_INTEGER = new AtomicInteger (0 ); @Override protected void encode (ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, RpcData rpcData, ByteBuf byteBuf) { try { int fullLengthIndex = encodeHead(rpcData,byteBuf); int fullLength = encodeBody(rpcData, byteBuf); encodeLength(fullLengthIndex,fullLength,byteBuf); } catch (Exception e) { LogUtil.error("Encode request error:{},data:{}" , e, rpcData); throw new RpcException (RpcErrorMessageEnum.REQUEST_ENCODE_FAIL.getCode(), RpcErrorMessageEnum.REQUEST_ENCODE_FAIL.getMessage()); } } private int encodeHead (RpcData rpcData,ByteBuf byteBuf) { byteBuf.writeBytes(RpcConstants.MAGIC_NUMBER); byteBuf.writeByte(RpcConstants.VERSION); int fullLengthIndex = byteBuf.writerIndex(); byteBuf.writerIndex(byteBuf.writerIndex() + 4 ); byteBuf.writeByte(rpcData.getMessageType()); byteBuf.writeByte(rpcData.getSerializeMethodCodec()); byteBuf.writeByte(rpcData.getCompressType()); byteBuf.writeInt(ATOMIC_INTEGER.getAndIncrement()); return fullLengthIndex; } private int encodeBody (RpcData rpcData,ByteBuf byteBuf) { byte [] bodyBytes = null ; int fullLength = RpcConstants.HEAD_LENGTH; if (rpcData.canSendRequest()) { LogUtil.info("serialize request start" ); bodyBytes = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(SerializationService.class) .getExtension(SerializationTypeEnum.getName(rpcData.getSerializeMethodCodec())) .serialize(rpcData.getData()); LogUtil.info("serialize request end" ); String compressName = CompressTypeEnum.getName(rpcData.getCompressType()); CompressService extension = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(CompressService.class).getExtension(compressName); bodyBytes = extension.compress(bodyBytes); fullLength += bodyBytes.length; } if (bodyBytes != null ) { byteBuf.writeBytes(bodyBytes); } return fullLength; } private void encodeLength (int fullLengthIndex,int fullLength,ByteBuf byteBuf) { int writeIndex = byteBuf.writerIndex(); byteBuf.writerIndex(fullLengthIndex); byteBuf.writeInt(fullLength); byteBuf.writerIndex(writeIndex); } }
request handling and invocation Here, netty’s SimpleChannelInboundHandler is used, which avoids the problem of resource release
As decoding has already been implemented earlier, it is only necessary to handle the request differently for different request types.
If it is a heartbeat request, the heartbeat response is returned
If it is a service request, the service is invoked via a dynamic proxy and the result is written and returned to the consumer.
Define a response class
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor @Data @Builder public class RpcResponse <T> implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 347966260947189201L ; private String requestId; private Integer code; private String message; private T data; public static <T> RpcResponse<T> success (T data, String requestId) { RpcResponse<T> response = new RpcResponse <>(); response.setCode(RpcResponseCodeEnum.SUCCESS.getCode()); response.setMessage(RpcResponseCodeEnum.SUCCESS.getMessage()); response.setRequestId(requestId); if (null != data) { response.setData(data); } return response; } public static <T> RpcResponse<T> fail () { RpcResponse<T> response = new RpcResponse <>(); response.setCode(RpcResponseCodeEnum.FAIL.getCode()); response.setMessage(RpcResponseCodeEnum.FAIL.getMessage()); return response; } }
The core method of the serverhandler is channelRead0.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 public class NettyRpcServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler <RpcData> { private final RpcRequestHandler rpcRequestHandler; public NettyRpcServerHandler () { this .rpcRequestHandler = SingletonFactory.getInstance(RpcRequestHandler.class); } @Override public void userEventTriggered (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception { if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) { IdleState state = ((IdleStateEvent)evt).state(); if (state == IdleState.READER_IDLE) { LogUtil.info("idle check happen, so close the connection" ); ctx.close(); } } else { super .userEventTriggered(ctx, evt); } } @Override public void exceptionCaught (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) { LogUtil.error("server exceptionCaught" ); cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcData rpcData) throws Exception { LogUtil.info("Server receive message: [{}]" , rpcData); RpcData rpcMessage = new RpcData (); setupRpcMessage(rpcMessage); if (rpcData.isHeatBeatRequest()) { handleHeartbeat(rpcMessage); } else { handleRpcRequest(ctx, rpcData, rpcMessage); } ctx.writeAndFlush(rpcMessage).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE); } private void setupRpcMessage (RpcData rpcMessage) { rpcMessage.setSerializeMethodCodec(SerializationTypeEnum.HESSIAN.getCode()); rpcMessage.setCompressType(CompressTypeEnum.GZIP.getCode()); } private void handleHeartbeat (RpcData rpcMessage) { rpcMessage.setMessageType(RpcConstants.HEARTBEAT_RESPONSE_TYPE); rpcMessage.setData(RpcConstants.PONG); } private void handleRpcRequest (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcData rpcData, RpcData rpcMessage) throws Exception { RpcRequest rpcRequest = (RpcRequest)rpcData.getData(); Object result = rpcRequestHandler.handle(rpcRequest); LogUtil.info("Server get result: {}" , result); rpcMessage.setMessageType(RpcConstants.RESPONSE_TYPE); buildAndSetRpcResponse(ctx, rpcRequest, rpcMessage, result); } private void buildAndSetRpcResponse (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcRequest rpcRequest, RpcData rpcMessage, Object result) { if (canBuildResponse(ctx)) { RpcResponse<Object> rpcResponse = RpcResponse.success(result, rpcRequest.getTraceId()); rpcMessage.setData(rpcResponse); } else { RpcResponse<Object> rpcResponse = RpcResponse.fail(); rpcMessage.setData(rpcResponse); LogUtil.error("Not writable now, message dropped,message:{}" , rpcRequest); } } private boolean canBuildResponse (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { return ctx.channel().isActive() && ctx.channel().isWritable(); } }
tipp: Services that are cached after registration to zk can be called directly based on dynamic proxies
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public class RpcRequestHandler { private final RpcServiceRegistryAdapter adapter; public RpcRequestHandler () { this .adapter = SingletonFactory.getInstance(RpcServiceRegistryAdapterImpl.class); } public Object handle (RpcRequest request) { Object service = adapter.getService(request.fetchRpcServiceName()); return invoke(request, service); } private Object invoke (RpcRequest rpcRequest, Object service) { Object result; try { Method method = service.getClass().getMethod(rpcRequest.getMethodName(), rpcRequest.getParamTypes()); result = method.invoke(service, rpcRequest.getParameters()); LogUtil.info("service:[{}] successful invoke method:[{}]" , rpcRequest.getServiceName(), rpcRequest.getMethodName()); } catch (NoSuchMethodException | IllegalArgumentException | InvocationTargetException | IllegalAccessException e) { LogUtil.error("occur exception when invoke target method,error:{},RpcRequest:{}" , e, rpcRequest); throw new RpcException (RpcErrorMessageEnum.SERVICE_INVOCATION_FAILURE.getCode(), RpcErrorMessageEnum.SERVICE_INVOCATION_FAILURE.getMessage()); } return result; } }
At this point, a server-side code is complete