Q:
Given an integer n, return all the numbers in the range [1, n] sorted in lexicographical order.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time and uses O(1) extra space.
S:
First: the dictionary order can be abstracted as a tree, as shown in the following figure
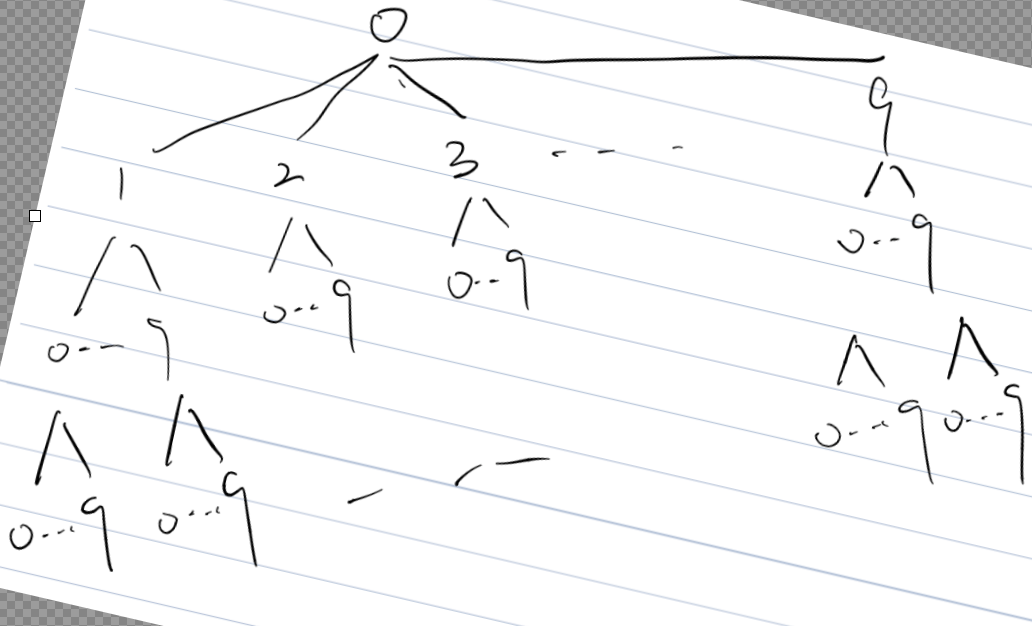
So, there is a small to large output is actually the output of his prior traversal
Reference to the prior-order traversal of the binary search tree write
- Recursion:
The difference here is the need to round off the head node 0, to 1-9 respectively as the root node for traversal output: 1:
recursion end condition, the current node > n, the recursion ends
add the element value into res, traverse its 10 sibling nodes, enter the recursion of its child nodes
1 | class Solution { |
2.迭代:
\2. Iteration .
tipp : while(curr%10==0) curr/=10; The purpose of this line of code is to handle numbers that should end early in the dictionary order.
For example, suppose n is 130. When we traverse through the dictionary order, it should be in this order: 1, 10, 11, … , 19, 2, 20, … , 19, 2, 20, … , 29, … , 13, 130, 14, … , 19, 2, … , 9.
After our curr becomes 130, if we directly curr+=1, then curr becomes 131, which is obviously more than n and does not fit the dictionary order. We should skip all 13x (x > 0) numbers and just become 14.
This is the purpose of the line while(curr%10==0) curr/=10;:
when the last digit of curr is 0 (i.e. curr%10==0), we should fall back to the previous level (i.e. curr/=10). In this example, 130 falls back to 13, and then curr+=1 becomes 14, so that it is in dictionary order.
This treatment ensures that our traversal order is always in dictionary order, i.e., we traverse
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class Solution {
public List<Integer> lexicalOrder(int n) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int curr = 1;
// 遍历/traverse
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
list.add(curr);
if(curr*10<=n){
curr*=10;//遍历下一层/find next level number
}else{
if(curr>=n) curr/=10;//如果比n大,结束遍历退回上一层/If greater than n, end traversal and return to previous level
curr+=1;
while(curr%10==0) curr/=10;
}
}
return list;
}
}